ISSN 2410-5708 / e-ISSN 2313-7215
Year 13 | No. 38 | October 2024- January 2025
© Copyright (2024). National Autonomous University of Nicaragua, Managua.
This document is under a Creative Commons
Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International licence.
Efficacy of educational intervention in healthy lifestyles in patients with Arterial Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus, who attend the health post, Buena Vista municipality of La Conquista, Carazo, Nicaragua, in January - February 2023.
https://doi.org/10.5377/rtu.v13i38.19324
Submitted on july 3rd, 2023 / Accepted on october 16th, 2024
Traña Aburto, Darling Suyen
Master's Degree in Public Health, Center for Research and -
Health Studies, CIES/UNAN-MANAGUA.
Lacayo Lacayo, Sofía
Master's Degree in Public Health, Center for Research and -
Health Studies, CIES/UNAN-MANAGUA.
Section: Health and Social services
Scientific research article
Keywords: Lifestyles, Intervention, Hypertensive patients, Diabetic patients.
Abstract
High blood pressure and diabetes mellitus are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the world, causing about half of all deaths from stroke and heart disease, being one of the most frequent public health problems. In Nicaragua, “the first cause (of medical care) continues to be hypertension.” Approximately 222 thousand people indicated and are verified from the visit of our health personnel, as the first cause of attention or need to be attended by the health services; the second is diabetes mellitus. To evaluate the effectiveness of educational intervention in healthy lifestyles in patients with high blood pressure and diabetes who attend the Buena Vista health post in La Conquista, Carazo, Nicaragua, from January-February 2023. A mixed longitudinal study was carried out with 65 diabetic and hypertensive patients, taking into account the inclusion criteria and taking a sample of 52 patients. According to sociodemographic characteristics, it was found that the largest number of patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus are adults over 56 years of age, of rural origin, with an incomplete level of primary schooling, with the most predominant sex being women with 63%. The poor practice of healthy lifestyles is what leads to suffering from high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus, due to unhealthy habits contributing to complications, we must take into account the importance of chronic disease prevention programs through the (MOSAFC) with an emphasis on health promotion and prevention.
INTRODUCTION
High blood pressure and diabetes mellitus are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the world, accounting for about half of all deaths from stroke and heart disease, making it one of the most common public health problems. Hypertension is the main risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Every year, 1.6 million deaths from cardiovascular diseases occur in the Region of the Americas, of which about half a million are people under 70 years of age, which is considered an early and preventable death. (Washington, D.C.: PAHO; 2019)
Diabetes mellitus is a leading cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, strokes, and lower limb amputation. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the chances of these complications and premature mortality. In addition, people with diabetes are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease and tuberculosis, especially those with poor glycemic control.
In Nicaragua, “the first cause (of medical care) continues being hypertension” Approximately 222 thousand people indicated and are verified from the visit of our health personnel, as the first cause of attention or need to be attended by health services; the second is diabetes mellitus. (MINSA, 2022)
The objective is to evaluate the efficacy of educational intervention in healthy lifestyles in patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus who attend the Buena Vista health post in La Conquista, Carazo, Nicaragua, during February 2023.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Type of study:
A longitudinal mixed study analyzes the efficacy of educational interventions in patients diagnosed with Arterial Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus through data collection.
According to the research method, the present study is of a mixed type, (Hernández Sampieri et al. 2008). according to the period, time of occurrence of the events, sequence, and recording of the information in the study is longitudinal (Arnau, J. & Bono, R. (2008).
Study area:
Buena Vista Health Post, municipality of La Conquista.
Universe:
65 patients diagnosed with Arterial Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus, male and female, who attend the Buena Vista Health Post in the municipality of La Conquista, Carazo, January-February 2023.
Sample:
A sample of 52 patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus who attend the Buena Vista health post was determined, taking into account the selection criteria, it was calculated with Open Epi, version 3, the open-source calculator SSPropor with a confidence interval of 95%. We took into account inclusion criteria; the entire universe was not taken because patients who refused to participate in the study and did not attend the educational intervention workshops were excluded.
Population Size: 65
Anticipated frequency%: 50
Confidence limit: 1%
Design Effect: 1.0
The sample was calculated at 95% confidence
According to OPEN EPI (https://www.openepi.com/SampleSize/SSPropor.htm)
Unit of analysis:
Patients diagnosed with Arterial Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus who attend the Buena Vista health post, municipality of La Conquista, Carazo.
RESULTS
According to the objectives of the study, the following results were obtained.
FIGURE 1
Sex of patients diagnosed with high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus attending the Buena Vista health post, Carazo, Nicaragua, January-February 2023.
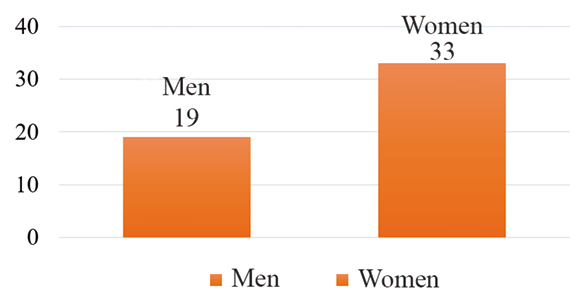
Source: Information collection instrument database.
The sex most affected are women: of the total of 52 patients diagnosed with high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus, 63% are equivalent to 33 women and 37% are equivalent to 19 men.
Schooling of patients diagnosed with high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus who attend the Buena Vista health post, Carazo, Nicaragua, January-February 2023.
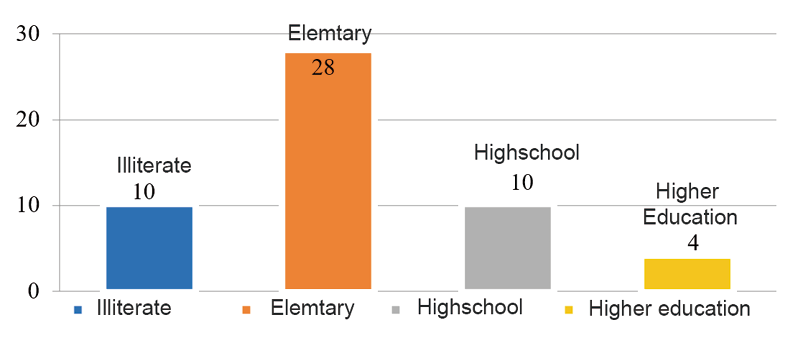
Source: Information collection instrument database.
The most affected level of schooling of the patients studied with arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus are those who have completed or incomplete primary school, 28 of the 52 patients studied.
Classification of the diseases they suffer according to the age of patients diagnosed with high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus who attend the Buena Vista health post, Carazo Nicaragua January-February 2023.
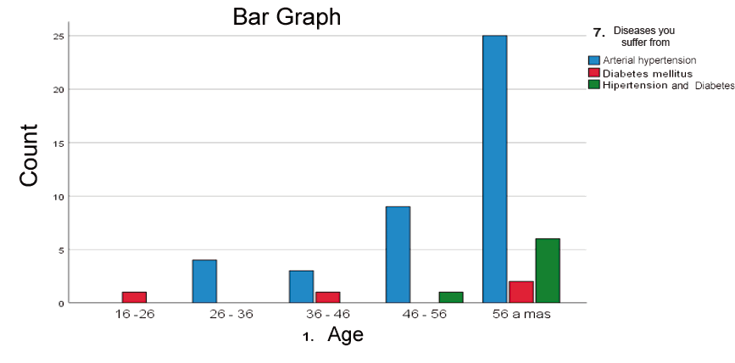
Source: Information collection instrument database.
According to the age of the patients studied, statistically it was found that the largest number of patients diagnosed with high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus are adults over 56 years of age, with a frequency of 33 patients studied belonging to this group.
FIGURE 4
Classification of the diseases they suffer according to the sex of patients diagnosed with high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus who attend the Buena Vista health post, Carazo Nicaragua February 2023.
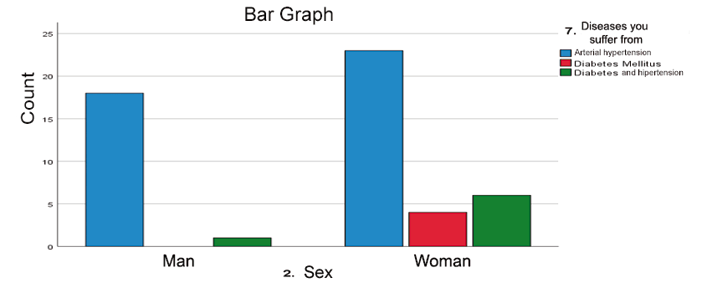
Source: Information collection instrument database.
According to the sex of the patients studied, the most predominant to suffer from high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus are women, with 33 of the 52 patients belonging to this group.
The frequency with which patients diagnosed with high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus attend the Buena Vista health post, Carazo, Nicaragua, January-February 2023, perform physical exercise before and after educational intervention.
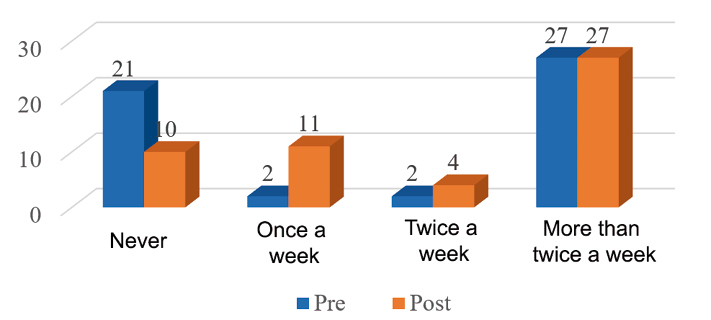
Source: Information collection instrument database.
According to the level of frequency with which the patients studied performed physical exercises before the intervention, we found that 51.9% exercised more than twice a week, while 40.4% never exercised and after the intervention, 19.2% never exercised, there was a significant change of 21.2% started exercising once a week.
FIGURE 6
The frequency with which patients diagnosed with high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus who attend the Buena Vista health post, Carazo, Nicaragua, January-February 2023 take 4-8 glasses of water per day, before and after educational intervention.

Source: Information collection instrument database.
The level of frequency with which the patients studied drank water before the intervention shows that 27 of the 52 patients drank 4-8 glasses of water daily, 17 sometimes and 6 frequently, and after the intervention, there was a significant change that 14 patients sometimes drink 4-8 glasses of water daily and 9 patients frequently.
Consumption of 3 meals breakfast, lunch, and dinner before and after educational intervention patients diagnosed with high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus who attend the Buena Vista health post, Carazo Nicaragua February 2023.
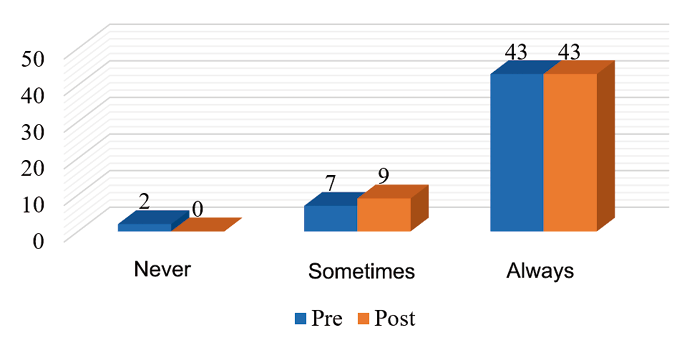
Source: Information Collection Instrument Database
According to the results obtained, we found that 82.7% ate three times a day, 13.5% sometimes, and 3.8% never, after the intervention 17.3% sometimes ate all three times and 82.75% always ate.
Table 1
Descriptive statistics of capillary glycemia levels before and after educational intervention patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus who attend the Buena Vista health post, Carazo Nicaragua February 2023.
|
Measures of central tendency and dispersion |
||
|
Descriptive statistics |
Pre Blood Glucose Test |
Post glycemia test |
|
Stocking |
170.64 |
128.36 |
|
Median |
167.00 |
129.00 |
|
Fashion |
124th |
112 |
|
Standard deviation |
46.760 |
15.933 |
|
Minimal |
124 |
110 |
|
Maximum |
295 |
147 |
|
Total |
11 |
11 |
Source: Information collection instrument database.
It can be observed that patients diagnosed with diabetes mellitus before the educational intervention had an average amount of 170.64 g/dl of capillary glycemia, with a minimum of 124 g/dl and a maximum of 295 g/dl and after the educational intervention the patients studied had an average of 128.36 g/dl with a minimum of 110 g/dl and a maximum of 147 g/dl.
Table 2
Descriptive statistics: systolic pressure and diastolic pressure values before and after educational intervention, patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus who attend the Buena Vista health post, Carazo, Nicaragua, January-February 2023.
|
Measures of central tendency and dispersion |
||||
|
Presión sistólica for. |
Presión diastólica for. |
Post systolic pressure. |
Post-diastolic pressure |
|
|
Media |
127.29 |
78.65 |
125.00 |
73.96 |
|
Median |
130.00 |
80.00 |
130.00 |
70.00 |
|
Standard deviation |
9.837 |
6.899 |
5.458 |
6.098 |
|
Minimal |
100 |
60 |
110 |
60 |
|
Maximum |
150 |
90 |
130 |
80 |
|
Total |
48 |
48 |
48 |
48 |
Source: Information collection instrument database.
It can be observed that patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension before the educational intervention had an average value of 127.29 systolic pressure, with a minimum of 100 and a maximum of 150 with an average value of 78.65 diastolic pressure, with a minimum of 60 and a maximum of 90 and after the educational intervention the patients studied had an average systolic pressure of 125.00, with a minimum of 110 and a maximum of 130, with an average value of 73.96 diastolic pressure, with a minimum of 60 and a maximum of 80.
Discussion of results
The sex most affected are women, of the total of 52 patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus, 63% with a frequency of 33 women and 37% with a frequency of 19 men. This result is related to the study by Reyes, M, Menéndez, L, Obregón, J, Núñez, M, García, E. (2020) Cuba. As for sex, the disease behaved with a higher number of cases in females with 53 patients (64.6%) over the male group, which were 29 (35.4%), according to them the differences are not significant, which rather related to other more frequent risk factors in one sex or the other: alcohol intake, stress, sedentary lifestyle, etc.
The most affected level of schooling of the patients studied with arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus are those who have completed or incomplete primary school, 28 of the 52 patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus. These results are related to the study by Doris, A, and Katheryne, Z, (2014) mention that 55% of the older adults in the Picsi 2013 Diabetes and Hypertension Program are female and 45% male, with the most affected level of schooling being those who completed primary school with 40%.
According to age, it was found that the largest number of patients diagnosed with high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus are adults over 56 years of age, with a frequency of 33. We relate it to the study by Dayna, O, Jacqueline, F, (2019) Chile the results of the study show that educational intervention is positively associated with favoring the achievement of therapeutic goals and improving glycemic control of the user with an average age of 63.3 years and 64.3 years for males.
According to the level of frequency with which the patients studied performed physical exercises before the intervention, we found that 51.9% exercised more than twice a week, while 40.4% never exercised, after the intervention 51.9% exercised more than twice a week, while 19.2% never exercise, there was a significant change of 21.2% who started exercising once a week. The week. We relate it to the Marlen G. (2020) study. It is possible to reflect that 64.6% (31) perform monthly physical activity, 25.0% (12) state that they perform physical activity weekly, and 10.4% (5) daily. It is also related to the study by Chambi J. (2018) that can be seen that most patients perform physical activity for less than 30 minutes, representing 65%, and where 15% of patients perform more than 30 minutes respectively and 20% perform 30 minutes of physical activity.
The level of frequency with which the patients studied drink water shows that 27 of the 52 patients drink 4-8 glasses of water daily, 17 sometimes, and 6 frequently, and then there was a significant change that 14 patients sometimes drink 4-8 glasses of water daily and 9 patients frequently of the total number of patients diagnosed with hypertension and diabetes mellitus. We relate it to the Chambi J. (2018) study shows that 50% of patients consume 1 to 2 glasses of water a day and 10% consume 5 to 6 glasses of water a day whereas the WHO ingests approximately 8 glasses of water a day to maintain good hydration.
According to the results obtained, we found that 82.7% ate three times a day, 13.5% sometimes, and 3.8% never, after the intervention 17.3% sometimes ate all three times and 82.7% ate all three times. According to the results obtained, the surveyed patients consume two or three times a day, the composition of a healthy diet depends on individual needs (e.g., age, sex, lifestyle, level of physical activity), cultural context, and locally available foods, they reported that they have a low diet due to the type of varied food they must consume due to the health condition they suffer, which has an impact on increasing the risk of suffering from chronic non-communicable diseases. These results are related to the study carried out in Washington, D.C. (PAHO, 2019).
It can be observed that patients diagnosed with diabetes mellitus before the educational intervention had an average amount of 170.64 g/dl of capillary glycemia, with a minimum of 124 g/dl and a maximum of 295 g/dl and after the educational intervention the patients studied had an average of 128.36 g/dl with a minimum of 110 g/dl and a maximum of 147 g/dl. We relate it to the study Doris, C, Rita, Z, Héctor, R, Rubén, C, (2019), Mexico. At baseline, only three people (7.7%) had the percentage of HbA1c in control [<7%], and at the end of the intervention, the number of people controlled increased to 10 (25.6%). The mean difference between before [9.25% ± 1.8 SD] and after [8.14% ± 1.7 SD] HbA1c was 1.11% [95% confidence interval: 0.7-1.15%], p<0.001.
It can be observed that patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension before the educational intervention had an average value of 127.29 systolic pressure, with a minimum of 100 and a maximum of 150 with an average value of 78.65 diastolic pressure, with a minimum of 60 and a maximum of 90 and after the educational intervention the patients studied had an average systolic pressure of 125.00, with a minimum of 110 and a maximum of 130, with an average value of 73.96 diastolic pressure, with a minimum of 60 and a maximum of 80. We relate it to the study
The nursing interventions carried out by health organizations are related to the modification of lifestyles, through health education, presenting participatory techniques that lead to awareness of the magnitude of the disease and the benefits that the intervention brings in modifiable factors. Puican, L, M (2019). They state that nursing interventions are carried out to make a change in the behavior or conduct of the lifestyle of each individual, which can be good or harmful to health.
Chronic, non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are the leading cause of death and disability in the world according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Many non-communicable diseases can be prevented by reducing common risk factors, such as tobacco use, harmful use of alcohol, physical inactivity, and eating unhealthy foods. Many other important conditions are also considered noncommunicable diseases, including injuries and mental health disorders.
CONCLUSIONS
It is concluded in this study that the most predominant sex to suffer from hypertension and diabetes mellitus are women with 63% with a frequency of 33 women and 37% with a frequency of 19 men, the most affected age are adults over 56 years of age, from rural areas with a low level of schooling of incomplete primary schooling. Most of them are not married and have a de facto relationship.
According to the results we obtained, we have that patients improved their healthy habits by highlighting physical activity, balanced eating, and complying with their medical appointments, this study promoted the culture of self-monitoring of glucose and blood pressure, self-care and lifestyle changes, training people living with diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure to recognize the relationship between knowledge and practice of healthy habits and to become aware of the positive or negative effects that come with making decisions about their habits and lifestyles. We must consider the importance of chronic disease prevention programs through the (MOSAFC) with an emphasis on health promotion and prevention.
The educational interventions on healthy lifestyles did have a positive impact on the patients studied, these results were statistically evidenced by the results obtained from the surveys that were carried out on patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus before and after the nursing interventions.
Work Cited
Galo M. (2020). Lifestyles in patients diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension who attend the “El Porvenir Medical Center” municipality of El Porvenir, Francisco Morazán, Honduras 2018-2020.
Alarcón, D, Zapata, K, (2013). Nursing educational intervention in healthy lifestyles, food, and exercise of the elderly. http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12423/440
Bermúdez J, (2017). Evaluation of an educational intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. National Diabetic Institute. Tegucigalpa MDC. file:///C:/Users/dsuye/Downloads/TESIS-DRA.-JOHANA-BERMUDEZ.pdf
Library of the National Congress of Chile. (01 of 03 of 2021). Retrieved from https://www.bcn.cl/portal/leyfacil/recurso/concejales
Reyes CMC, Menéndez GL, Obregón PJN, (2021). Effectiveness of an educational intervention to modify knowledge about lifestyles in hypertensive patients. EduMeCentro. 2021; 13(1):149-166.
Canché, A, L, Zapata, V, D, Rubio, Z, R, H, Cámara, V, R, (2019). Effect of an educational intervention on lifestyle, glycemic control, and knowledge of the disease, in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus, Bokobá, Yucatán. BIOMEDICAL JOURNAL. 30. 3-11. 10.32776/revbiomed.v30i1.654.
Pan American Health Organization. Core Indicators 2019: Health Trends in the Americas. Washington, D.C.: PAHO; 2019.
Martínez, M, Ramírez, C, Spain (2016). Health education intervention in cardiovascular diseases in the Penitentiary Center of Soria | Rev. esp. sanid. penit; 18(1): 5-12, 2016. Tab, Ilus | IBECS (bvsalud.org)
Ministry of Health (MINSA). Diabetes Mellitus Care Protocol. Government of Nicaragua. 2017.
González, P, Alvara, S, Martínez, R, Ponce, R. Mexico (2007). Level of knowledge about their disease in type 2 diabetic patients of the first level of medical care. Gac Méd Méx. 2007; 143(6): 453-62. http://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/gaceta/gm-2007/gm076a. pdf
León, M, Araujo, G, Linos, Z, (2012). Efficacy of the diabetes education program on clinical and biochemical parameters. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2012 Jan; 51(1): 74-9.
Estrella, K, Falcon, C, (2015) Peru. “Effectiveness of the promotion of healthy lifestyles in the health of the elderly of the C.I.A.M – Provincial Municipality of Pasco.
Rivera S, G. E. (2019). “Factors associated with arterial hypertension in patients who attend the chronic program in the municipality of Cua Jinotega. Matagalpa.